Table of contents:
- Production planning – definition. What is it?
- Basic concepts in production planning
- Types of production planning in a company
- What is production scheduling and why is a planner important?
- Knowledge of demand as an essential element of production planning
- Phases of production planning – how to create a schedule that fits the conditions of the organization?
- Production planning using the example of SAP S/4HANA
- How will the implementation of SAP S/4HANA with Hicron support your organization in production management?
When designing a schedule that will bring sales success to the organization, it is worth using the support of proven and efficient ERP systems. Practical knowledge alone is not enough to avoid complications in the production process. Again, cloud solutions are proving to be a great help. So how to plan tactically and make the most of these proven tools? It is worth starting from the beginning.
Production planning – definition. What is it?
Production planning is a mandatory process in every production company. It is a procedure for managing assortment, both future and existing. This includes:
- availability of materials,
- technological conditions of the enterprise,
- productivity and the number of employees and their efficiency,
- product demand,
- time considerations,
- warehouse stocks (their levels and total capacity),
- product flow and any possible variables.
It helps to create a production strategy that generates the highest profits while optimizing production costs.
Basic concepts in production planning
A good understanding of the entire production process is fundamental when developing an optimal strategy. Therefore, before doing so, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the issues associated with this endeavor. The more knowledgeable the employees involved in the operation, the better the chances of success.
It is impossible to list them all, but the basic concepts that are directly related to the production process include:
- BOM (Bill of Materials) – a list of all components and materials related to the production of a given item. A source of information that helps to prepare not only the entire process of product / service creation, but also any possible repairs. It also supports the organization in specifying the demand for specific raw materials or parts and determining the available production resources;
- workstation load balancing – a forecast of the production capacity of a given workstation based on the loads specified in the schedule;
- ACT (average cycle time) – a process calculated on the basis of the average for a given product in a given unit of time;
- Work Center – represents the integrated processes, workstations, machines, and the people operating them who are involved at a specific point of production;
- technological documentation – a set of all documents with relevant information;
- FR (Failure Rate) – a numerical number of equipment and production line failures per unit of time;
- APS (Advanced Planning and Scheduling) – implemented in logistics and production planning in every aspect, i.e. short-, medium-, and long-term, using advanced IT systems; enable the preparation of a good production plan with the help of complex planning activities and optimized simulations.
Types of production planning in a company
Before an enterprise takes steps to start production processes and organize production planning, managers and strategic teams should establish its production capacity. Therefore, the relevant departments in the organization are expected to analyze the declared Customer needs – what they are, how often the organization receives specific orders, and how they are fulfilled.
It is also important to take the human factor into account. For example, it may turn out that some employees need additional training on how to operate the new machines. It may also be necessary to hire additional people. In such a case, it is extremely important to determine the production costs of given items as well as to prepare a strategy in a specific time horizon.
Once all these details are determined, the company can choose a specific model that fits the established production plan.
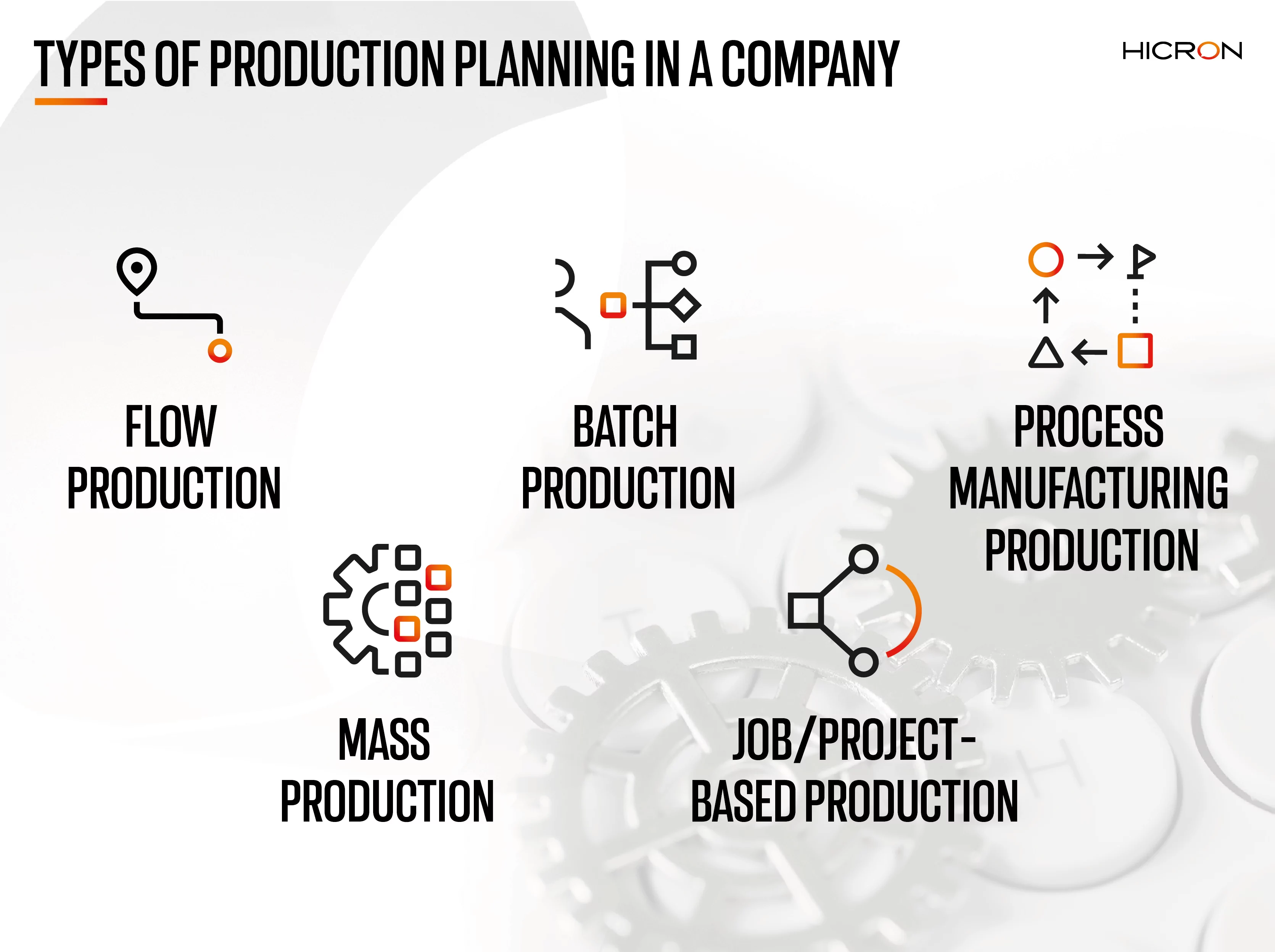
We are talking about the following types of production:
Flow production
It seeks to blur the boundaries between the different stages of production. The assumption is to create a production flow that eliminates all complications and possible delays. This type of production is based on maximum standardization and strict quality control at every point. This model works well for items that can be based on standard designs for each element. In order to prevent delays, it is important to remember about the availability of resources (e.g. human resources, materials, machines).
Batch production
This planning model is based on the production of individual elements in groups. It allows you to precisely control every moment in the production of an item. It involves monitoring and preventing any potential errors, and if they do occur, fixing them quickly. With this model, defects associated with one production batch can be eliminated in the next. However, to avoid bottlenecks and any delays, this production plan must take into account the availability of machinery and equipment. Some will work faster and make more products, while others will be slower. It is therefore worth analyzing the arrangement of work centers and their appropriate equipment.
Process manufacturing production
The assumption of this model is to automate production as much as possible while maintaining smooth transitions between its successive stages. In this case, special attention should be paid to controlling the undertaking on an ongoing basis, so that each item produced meets the standards adopted by the company. After all, one production error can affect a significant number of products. In process manufacturing, planning can concern the work of both employees and equipment.
Mass production
This model is close to flow production. However, it requires increased automation and divides production lines so that each is responsible for the production of one specific product. This type of planning saves production companies time that would otherwise be spent retooling production lines. Unlike the batch plan, this one is not broken down in such detail. The creation of a finished product does not involve its prior division into batches. This strategy also allows for faster production of items. When using this planning, it is worthwhile to control stocks in warehouses and organize production to avoid surpluses. Therefore, in this case, it is important to study market demand.
Job/project-based production
This method includes items whose individual parts are assigned to a distinct and strictly defined production plan. They are often prepared separately. In this case, the work is based on projects whose prior precise definition facilitates the entire undertaking. Such planning is typical of smaller plants focusing on high-precision, multi-component production. Therefore, one or very few people may be responsible for the production process of one part of the finished item. Such a model is used, for example, in the production of jewelry.
What is production scheduling and why is a planner important?
Often the terms “planning” and “production scheduling” are used interchangeably. This is a mistake, because there are crucial differences between them. The latter concept refers to the design of the production calendar on which the entire process is to be based. Organizing such a timetable is based on very detailed scheduling of production in the short term. In this approach, it is important to first determine the sequence of operational activities related to technology, i.e. taking into account specific machines, resources (including human resources), production lines, as well as those related to translating production into the realities of shift work.
Such ordering of production stages involves specifying the sequence of production activities using company resources. When creating a production schedule, it is very important to take into account the possible need to train employees, the cost of retooling the production line, issues related to preparation and completion in each production area, or any possible downtime (those that depend on the specifics of the plant and those that happen randomly).
It should be noted that the main production schedule is the result of careful work by the planner. Sometimes one person is responsible for this area, but in some cases a company may need to create an entire planning department. The tasks of these employees primarily include deciding on the sequence of relevant procedures, the size of batches prepared for production, preparing new transport routes in case of defects or accidents, or the order and quantity of products to be made.
Sometimes one organization employs several planners who are required to work together. Then they often decide on issues such as the use of equipment or technology to which access is limited, for example, when there is only one machine and its use is necessary for several projects. Such a person should demonstrate good communication skills to set up scheduling details without major complications and closely supervise orders with the support of other specialists in the production plant. Their role is very important and makes the production line work as intended.
Knowledge of demand as an essential element of production planning
The number of items produced is largely determined by this factor. Proper production planning is centered around this issue. How many Customers are interested in the product, what is the demand for it, how many competitors the company has on the market, as well as knowledge of the volume of orders from those interested in a particular batch – all this helps to determine the start date of production, its size, the need for proper resources, production capacity, the schedule itself, and many other aspects. Long-, medium-, and short-term demand should be considered.
The former usually covers a period of twelve months and is mainly related to determining the budget for production and the profits it will bring, as well as specifying the team’s capabilities and the need to hire new members.
The second involves a period of three to six months. It concerns the use of minimum stock levels in the plant’s warehouses, as well as items reserved for Customers in relation to their reported and expected needs. These figures are usually rounded to match those indicated in long-term demand. However, there are times when buyers’ needs are greater than originally anticipated. Then the managers of this area prepare new calculations and revise the budget, determine the availability of machines, specific positions, and resources.
The third concerns a much shorter period – a few weeks, a week, or even a few days. It includes only approved orders and stocks resulting from their minimum required levels. In the case of short-term demand, it is also important to ensure maximum load on machines and employees.
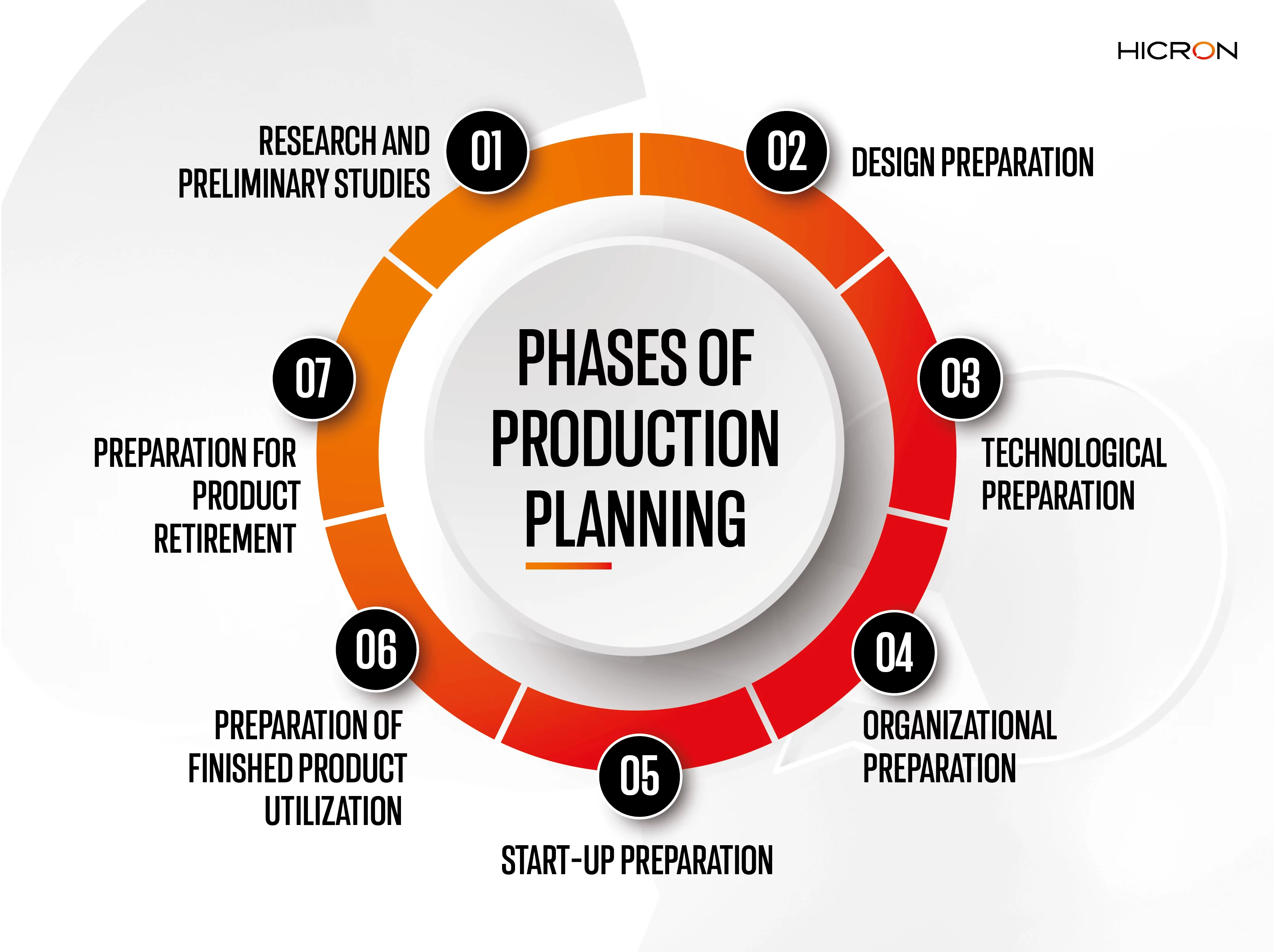
Phases of production planning – how to create a schedule that fits the conditions of the organization?
An extremely important aspect for any production company at the time of strategy development is the understanding and proper development of the subsequent production phases. This includes:
- Research and preliminary studies – involving the observation of marketing and market conditions related to the demand for a particular product.
- Design preparation – includes the design phases regarding the appearance and functionality of all parts as well as the finished product and the preparation of its test version.
- Technological preparation – refers to the development and operation of areas related to production.
- Organizational preparation – related to the organization of the work of all factory cells in which the process of item production will take place; this consists in the appropriate arrangement and preparation of workstations, proper delegation of tasks to specific teams, setting specific frameworks and deadlines assigned to specific procedures, preparation of employees, as well as development and determination of technological production processes and the systems used to manage them.
- Start-up preparation – includes all works necessary to begin the start-up series aimed at achieving the production and organizational parameters that will be maintained after the start of stable production.
- Preparation of finished product utilization – development of a strategy for distribution, Customer service, repair and maintenance works, and the technical service department.
- Preparation for product retirement – refers to the processes involved in removing an item from production and operation by buyers; it involves ceasing the production of the item, releasing production capacity, as well as recycling and environmental protection.
Specifying and defining the successive phases of production is an essential step. This component of the production strategy cannot be overlooked. Its neglect or inadequate analysis and organization can destabilize the subsequent stages of production and thus cause difficulties in the implementation of the entire project.
Production planning using the example of SAP S/4HANA
Even the best strategies of companies planning the fulfillment of production orders will not succeed without the support of appropriate, secure, and proven systems. Following the principles of planning is not enough. When deciding to undertake a project as advanced as bringing a product to market, it is important to use tools that will help optimize each of the aforementioned stages of the production path. Of course, Excel and other popular programs can help, but this is not enough.
SAP S/4HANA is an excellent solution to streamline plant operations for such projects. The flow of information in the cloud ensures that it is updated in real time on all workstations and for every logged-in user. It also allows you to organize and fully control your stock limits, which increase or decrease at the appropriate points in the process.
It is also a remarkable convenience when it is necessary to replenish resources. The system keeps you informed about shortages, and even allows you to avoid them by automatically displaying a notification when the minimum stock of a given item is reached. In addition, this solution makes it possible to track product transportation routes, update information on Customer demand, and facilitate forecasting for future production batches.
In the case of SAP S/4HANA, there are virtually countless possibilities to support any organization. Together with the help of experienced specialists who know the system perfectly, it is possible to achieve satisfactory sales results and tremendous business growth.
Want to learn more about the benefits of SAP S/4HANA Cloud and expert strategies for its implementation? Reach for Hicron’s free e-book!