A plant is an operational area or a branch of a company.
A plant is embedded in the organizational structure as follows:
- A plant is assigned to one company code. A company code can have several plants.
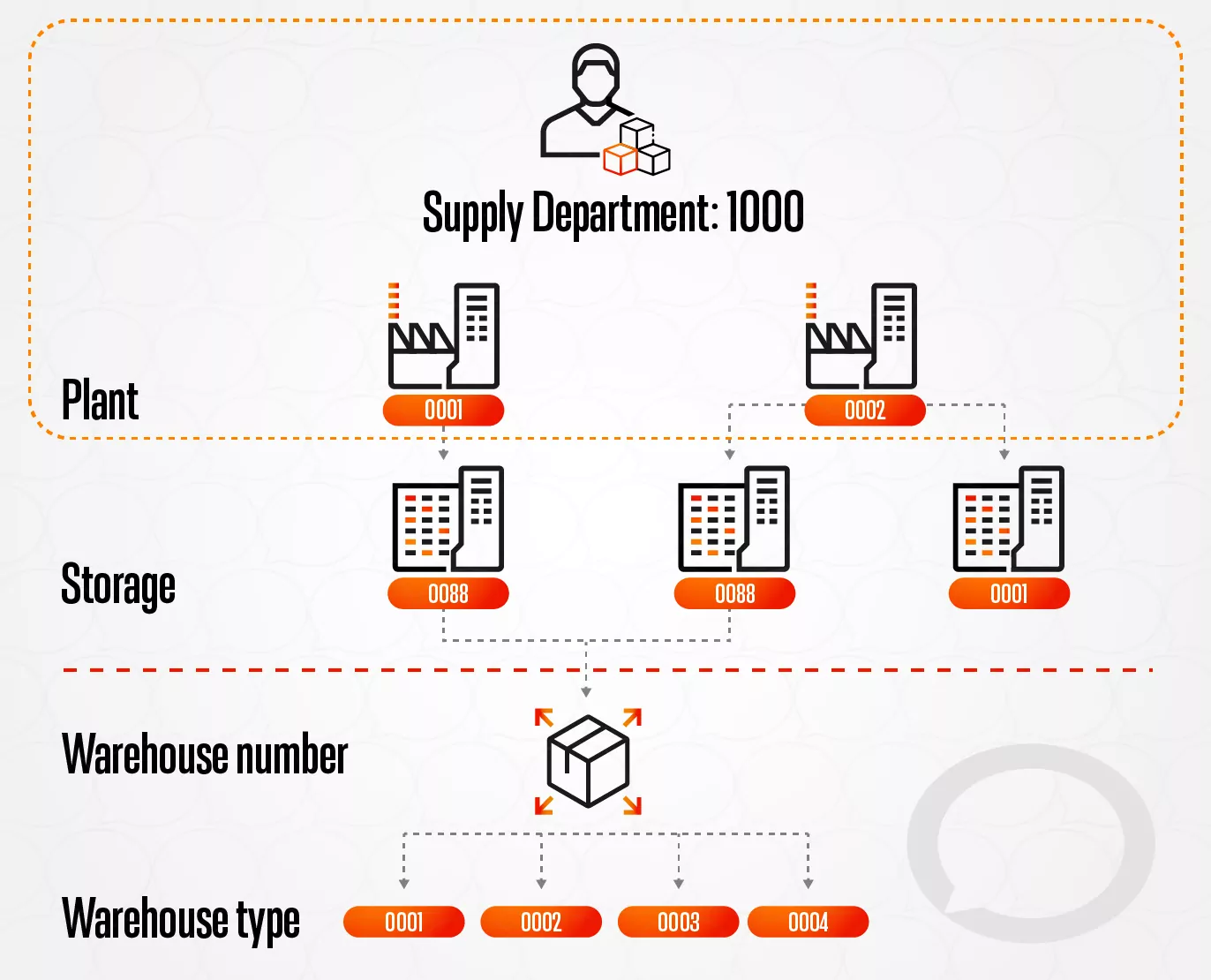
- One plant can have several storage locations where material inventories are managed.
- One business area is assigned to a plant and a branch.
- A plant can be assigned to several combinations of sales organization and distribution channel.
- A plant can have several shipping points. A shipping point can be assigned to several plants.
A plant has the following characteristics:
- it has an address;
- it belongs to a country;
- it has its own material master data. You can store data at the plant level specifically for the following material master record views: MRP, purchasing, warehousing, work planning, production resources/tools, forecasting, quality management, sales, cost calculation.
A plant plays an important role in the following areas:
- material valuation – if the valuation level is the plant, material inventories are valued at the plant level. You can define material prices for each plant. Each plant can have its own reconciliation account.
- inventory management – material inventories are managed within a plant.
- MRP – material requirements are planned for each plant. Each plant has its own MRP data. Material planning analyses can be performed across plants.
- production
- price analysis – cost calculations and valuations are defined only within a plant.
Example of a Structure for a Plant: