An ocean of possibilities
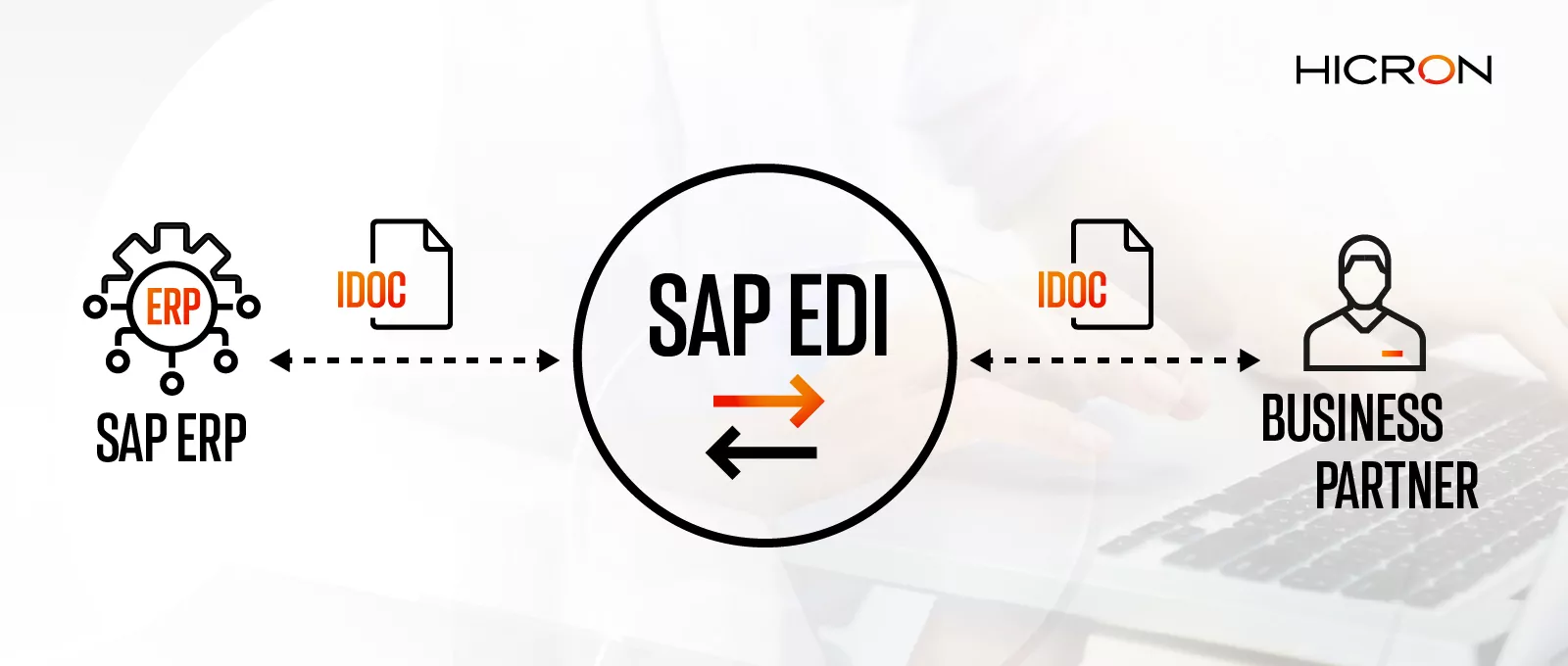
SAP EDI is a flexible and open solution that can be freely configured to meet even the most demanding needs. In addition to the typical transmission of invoices and orders, the solution can be configured in such a way that the client can be informed of the date of delivery, date and volume of production, which allows a production calendar for a specific client to be established, with full integration with the planning department. Below you can see a standard way of using EDI.

How does it work?
When using EDI, sales to customers are completed using scheduling agreements. Each client periodically sends the updated schedule of orders, usually covering a one-year time frame. On the basis of a schedule sent, shipments to the customer are made. The invoicing of shipments is also carried out.
1.Creating a scheduling agreement
The proposed process scenario requires that scheduling agreements must first be created manually in SAP by a sales/logistics employee. Creating the contract, an employee gives information about the customer, the customer scheduling agreement number, quantities of materials covered by the contract, the contract period.
2. Update of the delivery schedule – IDoc DELFOR
Then, through the EDI interface established before the current scheduling, agreements are automatically supplemented, updated periodically and transmitted by the customer delivery schedule in the form of an electronic document (IDOC) type DELFOR. For an incoming alert from a customer, an adequate open scheduling agreement regarding a particular material is searched for in SAP, and it is updated with the terms and amounts for shipping, specified by the customer.
As part of the agreement, it is possible to compare changes which have occurred in the updated shipping schedules (comparison of historical details and current shipping schedule to the contract).
Each incoming DELFOR alert is sent to an employee assigned to a particular customer in a form of an email informing them about a correctly booked EDI alert, an alert accepted in SAP, or an incorrectly processed alert. In the case of incorrectly booked idoc document e.g. due to the lack of an appropriate agreement in SAP or mistakenly assigned customer’s material number, the sales department employee will be able to complete the missing data and book or re-process the document manually.
3. Creating and booking a delivery
Creating a delivery shipment takes place only for confirmed terms and quantities from a particular schedule of shipments. The delivery is created manually by a sales/logistics employee in reference to the scheduling agreement. While creating a contract, the available stock of the sent material can be monitored. You can combine multiple scheduling agreements into a single delivery to the recipient. After creating the delivery in SAP, the booking of the issue of materials is processed by a sales/logistics employee.
4. Proof of delivery at the customer – IDoc DESADV
Booking a delivery automatically causes a shipping confirmation to be sent to the recipient via the EDI interface (DESADV alert). This message is determined as normal SAP output information from the header of the delivery document (there are standard formats established, e.g. goods dispatch note) which includes all the items found on the delivery document.
5. The invoice
Invoicing in SAP is completed manually by creating the invoice document with reference to the recorded delivery. The creation and booking of invoices will determine the appropriate output information in the header of the EDI invoices – INVOIC alert. At the moment of issuing the invoice, the prices will be updated again for a date pricing which by default are copied from the actual date of dispatch for the materials of the booked delivery document.
6. Sending an electronic invoice – INVOIC idoc
Sending an electronic invoice is run manually after it is booked, so that before sending this information it is possible to make amendments, for example, a reverse transactions invoice in case of errors in booking or price discrepancies.
How to implement EDI?
SAP EDI is based on standard technologies provided by SAP:
- SAP R/3 Standard interface, the so-called idoc interface, allowing for uniform handling of documents entering and leaving the system with a universal format;
- SAP Business Connector application, constituting a universal EDI subsystem (its licence is free to users of SAP R/3).
Each company which has implemented SAP system can use EDI without the cost of purchasing any additional licences. It is necessary only to configure the circulation of SD documents which ensures execution of scheduling agreements.
A wealth of benefits
The completed implementation of EDI solutions may lead to the following business benefits:
- Up-to-date, automatic data exchange (without replication, and without user involvement);
- Optimisation of the logistic chain;
- Unification of the purchase/sale functions between the partnering companies;
- Reduction of travel time devoted to the servicing purchase/sale transactions;
- Reduction in the number of errors in the servicing of transaction documents;
- Elimination of some hard copy documents;
- Streamlining of business procedures;
- Reduction of the time required to service orders through the rapid exchange of information and business data.





